 Home
Home
 Back
Back
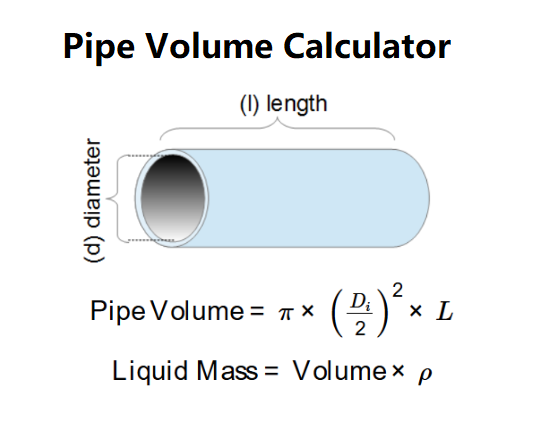
Advanced Definition: The Pipe Volume Calculator is an essential engineering tool that precisely calculates the internal capacity of cylindrical pipes and conduits. It determines both the volumetric capacity and, when required, the potential liquid mass based on fluid density properties.
Professional Applications: This calculator serves critical functions across multiple industries:
The calculator employs fundamental fluid mechanics and geometric formulas:
Technical Parameters:
Calculation Methodology:
Precise volume determination impacts multiple engineering disciplines:
Case Study 1: Municipal Water Supply (Metric Units)
| Parameter | Value | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Diameter | DN200 (200mm) | 0.2 m |
| Length | 500 m pipeline | 500 m |
| Volume | \( V = \pi \times (0.1)^2 \times 500 = 15.70796 \, \text{m}^3 \) | |
| Volume (Gallons) | \( 15.70796 \times 264.172 = 4149.2504 \, \text{gal} \) | |
| Water Mass | \( m = 15.70796 \times 1000 = 15,707.96 \, \text{kg} \) | |
Case Study 2: Industrial Fuel Line (Imperial Units)
| Parameter | Value | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Diameter | 8" Schedule 40 | 0.2027 m (7.981") |
| Length | 1,200 ft | 365.76 m |
| Diesel Density | 850 kg/m³ | 53.06 lb/ft³ |
| Volume | 11.804 m³ (416.77 ft³) | |
| Volume (Gallons) | \( 11.804 \times 264.172 = 3118.4065 \, \text{gal} \) | |
| Fuel Mass | 10,033.4 kg (22,120 lb) | |
Q: How does pipe material affect volume calculations?
A: While the calculator uses inner diameter, material properties determine:
Q: What about non-cylindrical pipes?
A: This calculator assumes perfect cylindrical geometry. For:
Q: How to account for multi-phase fluids?
A: For mixtures:
Professional Tip: Always include: