1. What is Pipe Drop Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the drop (\( d \)) at the end of a pipe run, which is the vertical distance the pipe must descend to maintain a desired grade, accounting for the pipe's outer diameter and an additional adder.
Purpose: It helps plumbers, engineers, and contractors ensure proper drainage or flow by calculating the necessary drop for a pipe run, especially in plumbing and irrigation systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equation:
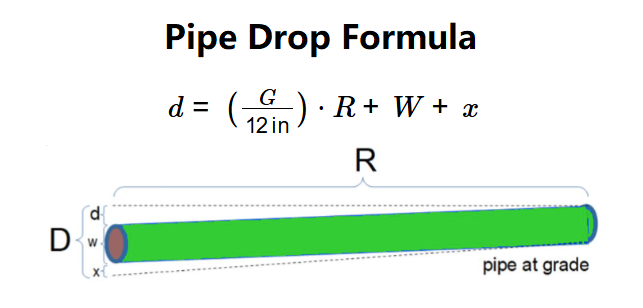
- \( d = \left( \frac{G}{12 \, \text{in}} \right) \cdot R + W + x \)
Where:
- \( G \): Drop per 12 inches (grade, in any unit);
- \( R \): Run length (in any unit);
- \( W \): Outer diameter of the pipe (in any unit);
- \( x \): Adder (additional drop, in any unit);
- \( d \): Total drop (in selected result unit);
- Results are displayed with 3 decimal places (or scientific notation if less than 0.001).
Steps:
- Select the drop per 12 inches (\( G \)) from the dropdown (1/8", 1/4", 1/2") or enter a custom value, and choose the unit (in, ft, yd, mm, cm, m).
- Enter the run length (\( R \)) and select the unit (in, ft, yd, mm, cm, m).
- Enter the outer diameter of the pipe (\( W \)) and select the unit (in, ft, yd, mm, cm, m).
- Enter the adder (\( x \)) and select the unit (in, ft, yd, mm, cm, m).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the total drop.
- Change the result unit dropdown to convert the drop value to a different unit.
3. Importance of Pipe Drop Calculation
Calculating pipe drop is crucial for:
- Proper Drainage: Ensures pipes slope correctly to allow gravity-driven flow, preventing clogs or backups.
- System Design: Helps in designing plumbing, sewer, or irrigation systems with the correct elevation changes.
- Installation Accuracy: Provides precise measurements for pipe installation, accounting for pipe diameter and additional factors.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the pipe drop with \( G = 0.25 \, \text{in} \), \( R = 10 \, \text{ft} \), \( W = 2 \, \text{in} \), \( x = 0 \, \text{in} \), result in yd:
- Drop per 12 inches: 0.25 in;
- Run Length: 10 ft (120 in);
- Outer Diameter: 2 in;
- Adder: 0 in;
- \( d = \left( \frac{0.25}{12} \right) \cdot 120 + 2 + 0 \);
- \( d = 0.020833 \cdot 120 + 2 = 2.5 + 2 = 4.5 \, \text{in} \);
- Convert to yd: \( 4.5 \div 36 = 0.125 \, \text{yd} \);
- Result: Drop = 0.125 yd.
Example 2: Calculate the pipe drop with \( G = 6 \, \text{mm} \), \( R = 3 \, \text{m} \), \( W = 50 \, \text{mm} \), \( x = 10 \, \text{mm} \), result in cm:
- Drop per 12 inches: 6 mm (0.2362 in);
- Run Length: 3 m (118.11 in);
- Outer Diameter: 50 mm (1.9685 in);
- Adder: 10 mm (0.3937 in);
- \( d = \left( \frac{0.2362}{12} \right) \cdot 118.11 + 1.9685 + 0.3937 \);
- \( d = 0.019683 \cdot 118.11 + 1.9685 + 0.3937 \approx 2.3248 + 1.9685 + 0.3937 \approx 4.687 \, \text{in} \);
- Convert to cm: \( 4.687 \times 2.54 \approx 11.905 \, \text{cm} \);
- Result: Drop = 11.905 cm.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Pipe Drop?
A: Pipe drop is the vertical distance a pipe descends over a given run length to maintain a desired slope or grade, often used in drainage systems.
Q: What does the adder represent?
A: The adder (\( x \)) is an additional drop to account for fittings, clearance, or other design requirements.
Q: Why include the outer diameter of the pipe?
A: The outer diameter (\( W \)) is added to the drop to ensure the pipe’s bottom aligns with the desired elevation, accounting for the pipe’s thickness.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back