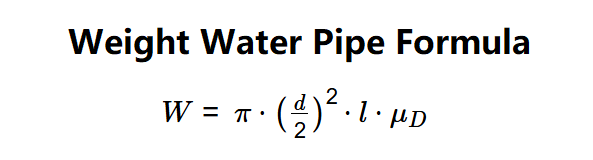1. What is Weight of Water in a Pipe Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the weight (\( W \)) of water (or another fluid) inside a cylindrical pipe by calculating the volume based on the inner diameter (\( d \)) and length (\( l \)), then multiplying by the density (\( \mu_D \)).
Purpose: It helps engineers and plumbers determine the weight of water in a pipe, useful for structural design, load calculations, and system planning.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equation:
- \( W = \pi \cdot \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 \cdot l \cdot \mu_D \)
Where:
- \( d \): Inner diameter of the pipe (in in, cm, or m);
- \( l \): Length of the pipe (in ft, m, or cm);
- \( \mu_D \): Mean density of the pipe contents (in kg/m³, g/cm³, or lb/ft³);
- \( W \): Weight of the water (in kg, lb, or g);
- Results are displayed with 3 decimal places (or scientific notation if less than 0.001).
Steps:
- Enter the inner diameter (\( d \)) of the pipe and select the unit (in, cm, m).
- Enter the length (\( l \)) of the pipe and select the unit (ft, m, cm).
- Enter the mean density (\( \mu_D \)) of the pipe contents (default is 1000 kg/m³ for water) and select the unit (kg/m³, g/cm³, lb/ft³).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the weight.
- Change the result unit dropdown to convert the weight to a different unit (kg, lb, g).
3. Importance of Weight of Water in a Pipe Calculation
Calculating the weight of water in a pipe is crucial for:
- Structural Design: Ensures pipes and supports can handle the weight of the water, preventing structural failure.
- System Planning: Helps in designing plumbing and irrigation systems by accounting for the load of the fluid.
- Safety Considerations: Prevents overloading in systems where pipes are suspended or elevated.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the weight with \( d = 2 \, \text{in} \), \( l = 10 \, \text{ft} \), \( \mu_D = 1000 \, \text{kg/m³} \), result in kg:
- Inner Diameter: 2 in = 0.0508 m;
- Length: 10 ft = 3.048 m;
- Density: 1000 kg/m³;
- \( W = \pi \cdot \left( \frac{0.0508}{2} \right)^2 \cdot 3.048 \cdot 1000 \);
- \( W = \pi \cdot (0.0254)^2 \cdot 3.048 \cdot 1000 \approx 6.176 \, \text{kg} \);
- Result: Weight = 6.176 kg.
Example 2: Calculate the weight with \( d = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( l = 2 \, \text{m} \), \( \mu_D = 1 \, \text{g/cm³} \), result in lb:
- Inner Diameter: 5 cm = 0.05 m;
- Length: 2 m;
- Density: 1 g/cm³ = 1000 kg/m³;
- \( W = \pi \cdot \left( \frac{0.05}{2} \right)^2 \cdot 2 \cdot 1000 \);
- \( W = \pi \cdot (0.025)^2 \cdot 2 \cdot 1000 \approx 3.927 \, \text{kg} \);
- Convert to lb: \( 3.927 \times 2.20462 \approx 8.657 \, \text{lb} \);
- Result: Weight = 8.657 lb.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Weight of Water in a Pipe?
A: It is the total weight of the water (or fluid) inside a pipe, calculated based on the pipe’s internal volume and the fluid’s density.
Q: Why is the density adjustable?
A: While water has a density of 1000 kg/m³, the calculator allows for different fluids or water with impurities, which may have different densities.
Q: Does this calculator account for the pipe’s weight?
A: No, this calculator only computes the weight of the water inside the pipe, not the pipe material itself.
Weight of Water in a Pipe Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back