1. What is Fluid Transit Speed Calculator?
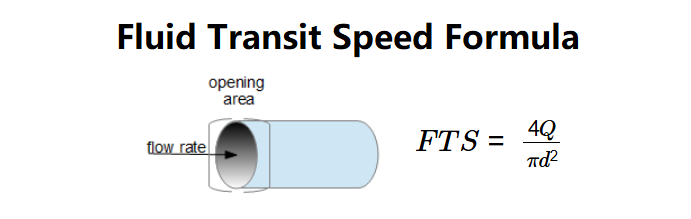
Definition: This calculator computes the fluid transit speed (\( FTS \)) in a conduit, based on the diameter of the conduit (\( d \)) and the flow rate (\( Q \)).
Purpose: It helps engineers determine the velocity of fluid flow in a pipe or conduit, which is essential for designing fluid transport systems, ensuring proper flow rates, and avoiding issues like turbulence or cavitation.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equation:
- \( FTS = \frac{4Q}{\pi d^2} \)
Where:
- \( d \): Diameter of the conduit (in m, mm, cm, in, ft, or yd);
- \( Q \): Flow rate (in m³/s, cm³/s, L/s, gal/s, gal/min, ft³/s, ft³/h, or m³/h);
- \( FTS \): Fluid transit speed (in m/s, ft/s, km/h, or mph);
- Results are displayed with 3 decimal places (or scientific notation if less than 0.001).
Steps:
- Enter the diameter of the conduit (\( d \)) and select the unit (m, mm, cm, in, ft, yd).
- Enter the flow rate (\( Q \)) and select the unit (m³/s, cm³/s, L/s, gal/s, gal/min, ft³/s, ft³/h, m³/h).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the fluid transit speed.
- Change the result unit dropdown to convert the speed to a different unit.
3. Importance of Fluid Transit Speed Calculation
Calculating the fluid transit speed is crucial for:
- System Design: Ensuring the fluid velocity is within acceptable limits to prevent erosion, cavitation, or excessive pressure drops.
- Flow Analysis: Determining whether the flow is laminar or turbulent, which affects system efficiency.
- Safety and Efficiency: Optimizing conduit sizes for energy-efficient fluid transport in pipelines, HVAC systems, or irrigation networks.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the fluid transit speed with \( d = 0.25 \, \text{m} \), \( Q = 1200 \, \text{m³/s} \), result in m/s:
- Diameter of Conduit: 0.25 m;
- Flow Rate: 1200 m³/s;
- \( FTS = \frac{4 \cdot 1200}{\pi \cdot (0.25)^2} \);
- \( (0.25)^2 = 0.0625 \), so \( FTS = \frac{4800}{\pi \cdot 0.0625} \approx \frac{4800}{0.196349} \approx 24446.199 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Result: Fluid Transit Speed = 24446.199 m/s.
Example 2: Calculate the fluid transit speed with \( d = 10 \, \text{in} \), \( Q = 5000 \, \text{gal/min} \), result in ft/s:
- Diameter of Conduit: 10 in = \( 10 \times 0.0254 = 0.254 \, \text{m} \);
- Flow Rate: 5000 gal/min = \( 5000 \times 0.0000630902 = 0.315451 \, \text{m³/s} \);
- \( FTS = \frac{4 \cdot 0.315451}{\pi \cdot (0.254)^2} \);
- \( (0.254)^2 \approx 0.064516 \), so \( FTS \approx \frac{4 \cdot 0.315451}{\pi \cdot 0.064516} \approx \frac{1.261804}{0.202632} \approx 6.227 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Convert to ft/s: \( 6.227 \times 3.28084 \approx 20.428 \, \text{ft/s} \);
- Result: Fluid Transit Speed = 20.428 ft/s.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Fluid Transit Speed?
A: It is the velocity at which a fluid travels through a conduit, determined by the flow rate and the conduit's cross-sectional area.
Q: Why is conduit diameter important?
A: The diameter affects the cross-sectional area; a smaller diameter increases the fluid speed for the same flow rate, potentially leading to higher pressure losses or turbulence.
Q: How does flow rate affect fluid transit speed?
A: The fluid transit speed is directly proportional to the flow rate; increasing the flow rate increases the speed, assuming the conduit diameter remains constant.
Fluid Transit Speed Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back